Türkische Quelljungfer
© Manci Cosmin-Ovidiu (Foto) & Clemens M. Brandstetter (Text)
 (from Boudot & al. 2009:151): Cordulegaster picta is an eastern Mediterranean species known from northeastern Greece and Bulgaria to Azerbaijan. A recent record from Montenegro extends the range 350 km to the north-west. Old records from north Italy and Dalmatia are believed to be incorrect. Similary, a record from the area of Athens in Greee is believed to be erraneous. Its habitat ranges from minute rivulets in dark forests to middle-sized rivers. Some localities are threatened due the climate change, habitat destruction and/or polution.
(from Boudot & al. 2009:151): Cordulegaster picta is an eastern Mediterranean species known from northeastern Greece and Bulgaria to Azerbaijan. A recent record from Montenegro extends the range 350 km to the north-west. Old records from north Italy and Dalmatia are believed to be incorrect. Similary, a record from the area of Athens in Greee is believed to be erraneous. Its habitat ranges from minute rivulets in dark forests to middle-sized rivers. Some localities are threatened due the climate change, habitat destruction and/or polution.
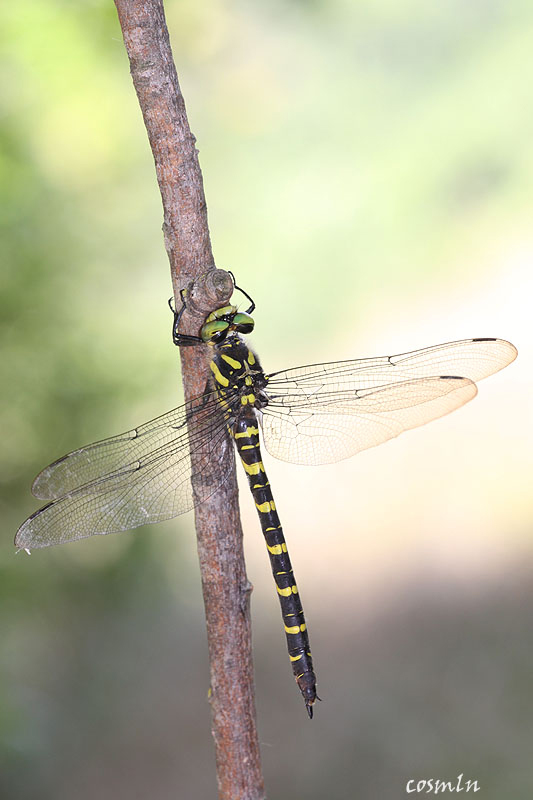
Die Türkische Quelljungfer, Cordulegaster picta Selys 1854, kommt in Griechenland, der Türkei bis Aserbaidschan vor. Sie bewohnt vor allem saubere Waldbäche. Ihre Augen sind zum Unterschied von C. insignis grünlich statt blau.
Froufe & al. (2014) präsentieren eine Studie über genetische Untersuchungen an der Gattung Cordulegaster. Die bisher traditionell unterschiedenen Artengruppen haben sich auch genetisch bestätigt: "Although Odonata are a key component of many freshwater ecosystems, their taxonomy and evolutionary history is still far from being well resolved. In the present study, we report the first molecular phylogeny for the Western Palaearctic Cordulegaster genus (Odonata: Anisoptera: Cordulegastridae). We sequenced fragments of both mitochondrial and nuclear genes [cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) and Internal Transcribed Spacer-1 (ITS-1)] from eight species and 13 subspecies, from western, southern and central Europe, Turkey, and Morocco. Our data support the existence of two major groups corresponding to the traditional boltonii– and bidentata-groups. Both groups are monophyletic based on COI sequences and the distinctiveness of Cordulegaster princeps, Cordulegaster trinacriae, Cordulegaster picta and Cordulegaster heros relative to Cordulegaster boltonii, and Cordulegaster helladica and Cordulegaster insignis relative to Cordulegaster bidentata, is confirmed. All species are also monophyletic for ITS-1, with the exception of Cordulegaster helladica buchholzi, which shares the haplotype with C. insignis. Although moderate levels of genetic diversity were found within C. boltonii, there was no clear separation among the four subspecies, with the exception of the populations of Cordulegaster boltonii algirica from North Africa. Similarly, no genetic differentiation was found between the two subspecies of C. bidentata, Cordulegaster bidentata bidentata and Cordulegaster bidenta sicilica.."

Schwarzmeerküste bei Dobrogea (Rumänien).
Literatur:
Boudot J.-P., V. J. Kalkman, M. Amorín, T. Bogdanović, A. Rivera,G. Degabriele, J.L. Dommanget, S. Ferreira, B. Garrigós, M. Jović, M. Kotarac, W. Lopau, M. Marinov, N. Mihoković, E. Riservato, B. Samraoui & W. Schneider 2009: Atlas of the Odonata of the Mediterranean and North Africa. – Libellula Supplement 9:1-256.
Froufe E., Ferreira S., Boudot J.-P., Alves P.C. & D. J. Harris 2014: Molecular phylogeny of the Western Palaearctic Cordulegaster taxa (Odonata: Anisoptera: Cordulegastridae). – Biolog. Journ. Linn. Soc. 111: 49,57.
